Atmospheric carbonyl sulfide as a novel tracer
Carbonyl sulfide is the most abundant and longest-lived reduced sulfur gas in the atmosphere with an average mixing ratio around 0.5 parts-per-billion (ppb) (Montzka, et al. 2007).
Sometimes carbonyl sulfide is abbreviated as OCS, emphasizing it chemical formula, or COS, emphasizing its similarity to CO2. At a Keck Institute for Space Studies workshop, Roisin Commane arm-wrestled Mary Whelan to determine whether "OCS" or "COS" should be considered the preferred abbreviation. Prof Commane won and OCS is now the more encouraged spelling. The fact that, in programming code, naming a variable "COS" can also overwrite the cosine function was also a strong argument.
COSANOVA is derived from Carbonyl sulfide (COS) as A NOVel tracer: Applied. It also loosely translates to "new thing". COSANOVA is a community of scientific researchers that use atmospheric measurements of carbonyl sulfide and other emerging methods in ecosystem science. COS or OCS observations are somewhat difficult to make, but have a wide range of important applications.
Sometimes carbonyl sulfide is abbreviated as OCS, emphasizing it chemical formula, or COS, emphasizing its similarity to CO2. At a Keck Institute for Space Studies workshop, Roisin Commane arm-wrestled Mary Whelan to determine whether "OCS" or "COS" should be considered the preferred abbreviation. Prof Commane won and OCS is now the more encouraged spelling. The fact that, in programming code, naming a variable "COS" can also overwrite the cosine function was also a strong argument.
COSANOVA is derived from Carbonyl sulfide (COS) as A NOVel tracer: Applied. It also loosely translates to "new thing". COSANOVA is a community of scientific researchers that use atmospheric measurements of carbonyl sulfide and other emerging methods in ecosystem science. COS or OCS observations are somewhat difficult to make, but have a wide range of important applications.
OCS as a tracer for Gross Primary Production (GPP)
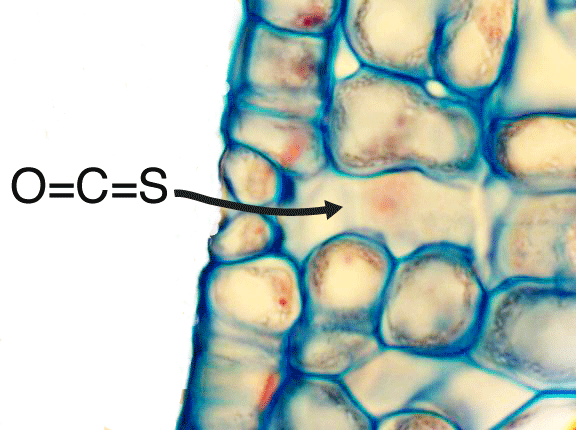
Many researchers began measuring OCS because it could potentially provide information about GPP. Measuring photosynthetic uptake of CO2 over ecosystems is problematic because as CO2 is being consumed by plants, it is also respired by roots and microorganisms.
The largest fluxes of OCS to the atmosphere is from the ocean and specific anthropogenic activities. The largest sink of OCS and CO2 is into plant leaves on land. Both CO2 and OCS interact with enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Under certain conditions, the uptake of CO2 by plant leaves occurs in a predictable ratio to OCS. Measuring the draw down of atmospheric OCS over ecosystems could provide some information about photosynthetic uptake.
The largest fluxes of OCS to the atmosphere is from the ocean and specific anthropogenic activities. The largest sink of OCS and CO2 is into plant leaves on land. Both CO2 and OCS interact with enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Under certain conditions, the uptake of CO2 by plant leaves occurs in a predictable ratio to OCS. Measuring the draw down of atmospheric OCS over ecosystems could provide some information about photosynthetic uptake.
Plant PhysiologyCarbonyl sulfide is taken up through plant stomata and interacts with the enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA). Questions about the activity of CA and the state of plant stomata could be queried by examining leaf level OCS fluxes. Isotopic labeling of OCS could also shed some light on in-leaf interactions.
|
Atmospheric dynamicsCarbonyl sulfide is relatively inert in the troposphere except for a strong sink term from vegetation. Observations of OCS concentrations can show whether a parcel of air has interacted with the terrestrial surface. There are also anthropogenic point sources that increase OCS concentrations in certain areas. Our understanding of source and sink terms can yield answers about atmospheric dynamics from OCS data.
|
Stratospheric sulfur budgetOCS is the longest lived of the sulfur compounds found in the troposphere. Between volcanic eruptions, much of the sulfur that reaches the stratosphere is in this form. OCS is transformed and contributes to the persistent layer of sulfate in the stratosphere that effects Earth's radiative balance. Examining OCS concentrations in the upper atmosphere can indicate air movement between the troposphere and the stratosphere. However, OCS should NOT be considered for geo-engineering schemes.
|
Global Sulfur CycleMost sulfur in the troposphere is the oxidized form, sulfate (SO4). Sulfate particles near the surface have short residence times. OCS is the most prevalent, naturally-occurring sulfur gas. Accounting for OCS fluxes over terrestrial and ocean ecosystems gives us a clearer view of the global sulfur cycle.
|